The Corona Crisis. Engineered Economic Depression
“The confinement of the labor force” coupled with “The paralysis of the workplace”. The predictable impact: The most serious economic crisis in world history.
To access Michel Chossudovsky’s Substack Archive
Dear friends and readers,
The text below is Chapter IV of my book entitled
The Worldwide Corona Crisis, Global Coup d’Etat Against Humanity
For substack readers it can be downloaded free of charge by clicking the download button.
ISBN: 978-0-9879389-3-0, Year: 2022, PDF Ebook, Pages: 164, 15 Chapters
Price: $11.50 Get yours for FREE! Click here to download.
Michel Chossudovsky reviews in detail how this insidious project “destroys people’s lives”. He provides a comprehensive analysis of everything you need to know about the “pandemic” — from the medical dimensions to the economic and social repercussions, political underpinnings, and mental and psychological impacts.
“My objective as an author is to inform people worldwide and refute the official narrative which has been used as a justification to destabilize the economic and social fabric of entire countries, followed by the imposition of the “deadly” COVID-19 “vaccine”. This crisis affects humanity in its entirety: almost 8 billion people. We stand in solidarity with our fellow human beings and our children worldwide. Truth is a powerful instrument.”
ISBN: 978-0-9879389-3-0, Year: 2022, PDF Ebook, Pages: 164, 15 Chapters
Price: $11.50 Get yours for FREE! Click here to download.
Author’s Note
The publication of my book was in August 2022.
Much of the analysis pertaining to the economic and social impacts was based on 2020-2021 data.
The March 11, 2020 (simultaneous) closing down of the national economies of approximately 190 member states of the UN is diabolical and unprecedented.
My thanks to readers who have sent a donation in support of my substack.
And our thanks to substack’s unbending and courageous support of independent media.
Hell is empty and all the devils are here.” ― William Shakespeare, The Tempest, 1610
“It’s A 21st Century Tempest:
“Let Us Ensure that the Devils Go Down to Where they Rightfully Belong”
Michel Chossudovsky, February 15, 2024
Below is an excerpt from the Preface followed by Chapter IV entitled
The Corona Crisis. Engineered Economic Depression
To consult Chapter V entitled
The Enrichment of the Super Rich. The Appropriation and Redistribution of Wealth. click the link to download the E-Book.
Preface
We are dealing with an exceedingly complex process. In the course of the last two and a half years, I have analyzed almost on a daily basis the timeline and evolution of the COVID-19 crisis.
From the very outset in January 2020, people worldwide were led to believe and accept the existence of a rapidly progressing and dangerous epidemic. Media disinformation was instrumental in sustaining the COVID-19 narrative.
At the time of writing, protest movements have erupted in numerous countries. The entire planet is in state of economic and social chaos. A worldwide crisis in food and agriculture is unfolding with famines erupting in all major regions of the world (see Chapter IV).
From the very outset in January 2020, scientific lies and falsehoods have been used to sustain the legitimacy of the COVID-19 policy mandates including lockdowns, the imposition of the face mask, social distancing and the suppression of fundamental human rights.
The decision-making process is controlled by the financial establishment. A structure of “Global Governance” is unfolding which undermines democracy and the institutions of civil society. The same instructions are transmitted simultaneously to corrupt politicians in a large number of countries. The United Nations system is also complicit in the conduct of this diabolical endeavor.
The pandemic was announced on March 11, 2020. On that same day, lockdown instructions were transmitted to 193 member states of the United Nations, essentially requiring the confinement of the labor force and the “closure” of the economic and social landscape as a means to “combating the virus”.
More than 7 billion people worldwide are directly or indirectly affected by the corona crisis and the destructive mandates implemented by morally depraved national governments.
The Corona Crisis. Engineered Economic Depression
Chapter IV of The Worldwide Corona Crisis, Global Coup d’Etat Against Humanity
Introduction
Economics 101. The March 11, 2020 lockdown applied simultaneously in 190 countries has resulted in:
“The confinement of the labor force” coupled with “The paralysis of the workplace”.
The predictable impact:
The most serious economic crisis in world history.
The Economics Profession
The economics profession focusing on the “market mechanism” has casually ignored this fundamental causal relationship.
The consensus among both neoclassical as well as “progressive” political economists and social scientists is that “V the virus”, namely SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the downfall of economic activity.
A similar position was adopted by trade union organizations including the AFL-CIO: the confinement of the labor force was viewed as a means to “protect” labor rights.
When workers are confined in their homes, prevented from going to their workplace, “the common sense impact” is obvious: the lockdown is conducive to worldwide economic and social chaos.
According to mainstream economists and financial analysts, the economic crisis commenced in early March 2022 coinciding with the onslaught of the war in Ukraine.
That position is mistaken.
The ongoing economic and social crisis which is affecting humanity worldwide has its roots in January 2020 following the WEF meetings in Davos and the launching of a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by the WHO (January 30, 2020).
Distinct Phases and Consequences
There are several distinct phases in the engineered destabilization of the global economy which are examined in this chapter:
-January 30, The WHO’s initial fraud:
The launching of a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) based on 83 Covid positive cases outside of China for a population of 6.4 billion.
“83 cases in 18 countries, and only 7 of them had no history of travel in China.” (See WHO, January 30, 2020)12
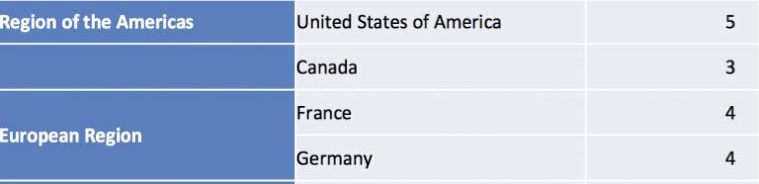
On January 29, 2020, the day preceding the launching of the PHEIC (recorded by the WHO), there were five cases in the US, three in Canada, four in France, and four in Germany.13
There was no “scientific basis” to justify the launching of a worldwide public health emergency.
Screenshot from WHO, January 29, 2020
- Late January 2020: the Trump administration announced (Jan 31, 2020) that the U.S. will deny entry to foreign nationals “who have traveled in China in the last 14 days”.1 Trump’s decision immediately triggered a crisis in air travel and transportation which is still ongoing. China-US trade as well as the tourism industry were disrupted.
- February 20, 2020: The WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros’s warning that a pandemic was imminent served to trigger the most serious financial crash since 1929.
-The March 11, 2020 lockdown was conducive to the “closing down” of approximately 190 national economies, with devastating economic and social consequences.
-November-December 2020: A partial lockdown as well as the launching of the COVID-19 vaccine
-November 2021-January 2022: The Omicron variant was used to justify a partial lockdown, the launching of the vaccine passport, the enforcement of restrictive measures directed against the unvaccinated.
-April-July 2022: The application of a lockdown mandate under China’s Zero Tolerance COVID Mandate in Shanghai and major urban areas in China.
The Disruption of US-China Trade
Trump’s decision on January 31, 2020 was taken immediately following the announcement of the WHO Director-General’s decision to launch a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) (January 30, 2020). In many regards, this was an act of “economic warfare” against China.
And then, following Trump’s January 31, 2020 decision to curtail air travel and transportation to China, a campaign was launched in Western countries against China as well as against ethnic Chinese. The Economist reported that “The coronavirus spreads racism against and among ethnic Chinese.”2
“Britain’s Chinese community faces racism over coronavirus outbreak.”
According to the South China Morning Post (Hong Kong): “Chinese communities overseas are increasingly facing racist abuse and discrimination amid the coronavirus outbreak. Some ethnic Chinese people living in the UK say they experienced growing hostility because of the deadly virus that originated in China.”3
US-China Trade. America’s Dependence on “Made in China”
The impacts on bilateral US-China trade relations at the outset of the corona crisis were devastating: US commodity imports from China declined by 28.3% in the course of the first three months of the corona crisis.
Following the March 11, 2020 lockdown and (partial) closure of economic activity worldwide, the decline of US imports from China in March 2020 was of the order of 36.5% (in relation to March 2019).4 Moreover, resulting from the deep-seated financial crisis which started in February 2020, the value of (announced) Chinese direct investment projects in the US had fallen by about 90% (Financial Times).5
While the US has an advanced and diversified high technology economy (in both civilian and military production), its manufacturing base is weak. America is an import-led economy (resulting from offshoring) heavily dependent on commodity imports from the People’s Republic of China.
Moreover, despite America’s financial dominance and the powers of the dollar, there are serious failures in the structure of America’s “real economy” which have been exacerbated by the corona crisis.
Political and geopolitical factors have also played a key role including the anti-Chinese campaign launched in February 2020 as well as threats by Washington, claiming that China was responsible for “spreading the virus”.
While the US economy entered into a deep-seated crisis starting with the February 2020 financial crash and the March 2020 lockdown, China’s national economy had recovered. China’s exports increased significantly in the course of 2021.
Bilateral US-China trade relations are nonetheless in jeopardy, marked by a significant reduction of Chinese imports from the US. While China’s exports to the United States increased in 2021, China’s monthly trade surplus with the United States increased by 31.1% (Time, January 14, 2022).6
In April 2022, there was a dramatic turnaround in China’s economy, marked by the adoption of a COVID-19 Zero Tolerance Mandate, (with millions of people confined to their homes) leading to a partial closing down of Shanghai’s financial sector coupled with a paralysis of commodity trade out the world’s largest port (see analysis below).
The February 2020 Corona Financial Crash
Speculative trade and financial fraud played a key role. On Thursday afternoon, 20th of February, in Geneva (CET Time), the WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus held a press conference. I am “concerned”, he said, “that the chance to contain the coronavirus outbreak” is “closing” ...
“I believe the window of opportunity is still there, but that the window is narrowing.”7
These “shock and awe” statements contributed to triggering panic, despite the fact that the number of confirmed cases outside China was exceedingly low: 1,076 cases for a population of 6.4 billion (excluding the Diamond Princess, there were 452 so-called “confirmed cases” worldwide) (see Chapter II).
The statement by Dr. Tedros (based on flawed concepts and statistics) set the stage for the February financial collapse triggered by inside information, foreknowledge, derivative trade, short-selling and a galore of hedge fund operations.
COVID-19 was narrowly identified as the catalyst of the financial crash. Who was behind this catalyst?
Who was behind the fear campaign which contributed to triggering chaos and uncertainty on financial markets?
The small number of “COVID-19 confirmed cases” outside China (1,076) did not in any way point to an unfolding worldwide epidemic. But this did not prevent the markets from plummeting.
The markets had been manipulated. Whoever had foreknowledge (“inside information”) of the WHO
Director-General’s February 20, 2020 statement would have reaped significant monetary gains.
Was there a conflict of interest (as defined by the WHO)?8 The WHO is partly funded by the Gates Foundation. Bill Gates has “60% of his assets invested in equities [including stocks and index funds]”, according to a September 2019 CNBC report.9
The stock market crash initiated on February 20th referred to as the 2020 Coronavirus Crash (February 20-April 7, 2020) was categorized as:
“the fastest fall in global stock markets in financial history, and the most devastating crash since the Wall Street Crash of 1929.”
The cause of the financial crash was (according to “analysts”) V the Virus, namely, the “massive spread” of the epidemic outside China. But that was an outright lie. There were only 1,076 cases worldwide for a population of 6.4 billion outside China (see Chapter III). Media disinformation played a key role in spearheading the fear campaign.
Insider Trading and Financial Fraud
The possibility of financial fraud and “insider trading” (which is illegal) was casually dispelled by financial analysts and media reports.
Without the human hand, there is no causal relationship between a microscopic virus and the complex gamut of financial variables.
The “killer virus” fear campaign coupled with Dr. Tedros’s timely “warnings” of the need to implement a worldwide pandemic indelibly served the interests of Wall Street’s institutional speculators and hedge funds. The financial crash led to a major shift in the distribution of money wealth (see analysis in Chapter V).
In the week following the February 20-21 WHO announcement, the Dow Jones collapsed by 12% (CNBC, February 28, 2020).10 According to analysts, the plunge of the DJIA was the result of the worldwide spread of the virus. A nonsensical statement in contradiction with the (small) number of WHO COVID positive estimates (1,076 outside China), most of which were based on the faulty PCR test.
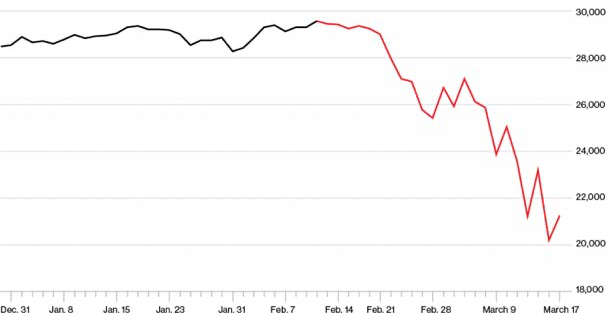
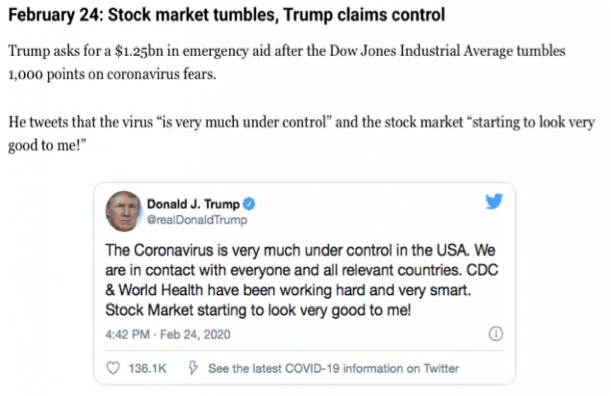
On Monday, February 24, upon the reopening of stock markets, there was an unprecedented plunge in the Dow Jones attributable to the “impending dangers” that “COVID was spreading worldwide creating uncertainties in financial markets”.
“Stocks fell sharply on Monday (February 24) as the number of coronavirus cases outside China surged, stoking fears of a prolonged global economic slowdown from the virus spreading. The Dow Jones Industrial Average closed 1,031.61 points lower, or 3.56%, at 27,960.80.” (CNBC) (emphasis added)
Dow Jones Industrial Average December 2019 – March 2020 (Source: Bloomberg Data)
Also on February 24, Trump requested a $1.25 billion emergency aid.
Screenshot from Al Jazeera
According to the BBC, worldwide stock markets saw sharp falls “because of concerns about the economic impact of the virus”, suggesting that the virus was “the invisible hand” responsible for the decline of financial markets.
COVID-19 was narrowly identified as the catalyst of the financial crash.
Who was behind the fear campaign which contributed to triggering chaos and uncertainty on financial markets coupled with bankruptcies and a massive redistribution of money wealth?
March 11, 2020: The COVID-19 Pandemic, Lockdown, Closing Down of 190 National Economies
On March 11, 2020, the WHO officially declared a worldwide pandemic at a time when the number of confirmed cases outside of China (6.4 billion population) was of the order of 44,279 and 1,440 deaths (figures recorded for March 11 by the WHO on March 12, 2020).11
The “science” behind this worldwide lockdown decision was based on “a mathematical model” by Dr. Neil Ferguson of Imperial College, London, as a means to avoiding a “predicted” 600,000 deaths in the UK.
Ferguson’s “model” (which borders on ridicule) was used by the financial establishment as a justification to trigger economic and social chaos worldwide. Ferguson’s endeavors were generously funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Immediately following the March 11, 2020 WHO announcement, the fear campaign went into high gear. As in the case of the February 20-21, 2020 crash, the March 11, 2020 statement by the WHO Director-General had set the stage.
Stock markets crashed worldwide. On the following morning, the Dow (DJIA) plummeted by 9.99% (a decline of 2,352.60 to close at 21,200.62). Black Thursday, March 12, 2020 was “the Dow’s worst day” since 1987.12 Financial fraud was the trigger. A massive transfer of financial wealth had taken place in favor of America’s billionaires (see chapter V).
“Stay at Home” confinement instructions were transmitted to 193 member states of the United Nations. Politicians are the instruments of powerful financial interests. Was this far-reaching decision justified as a means to combating the virus?
The decision was based on a flawed lockdown model designed by Imperial College London.
“Confinement of the labour force” coupled with paralysis of the “workplace” (productive, commercial activities, etc.) indelibly leads to a deep-seated worldwide economic depression.
Unprecedented in history, applied almost simultaneously in a large number countries, entire sectors of the world economy were destabilized. Small and medium-sized enterprises were driven into bankruptcy. Unemployment and poverty are rampant.
In several developing countries, famines have erupted (see analysis below). The social impacts of these measures are devastating. The health impacts (mortality and morbidity) including the destabilization of the national healthcare system (in numerous countries) far surpass those attributed to COVID-19.
Economic Warfare
The instructions came from above, from Wall Street, the World Economic Forum, and the billionaire foundations. This diabolical project is casually described by the corporate media as a “humanitarian” public health endeavor. The “international community” has a “Responsibility to Protect” (R2P). An unelected “public-private partnership” under the auspices of the World Economic Forum (WEF) has come to the rescue of planet Earth’s 7.9 billion people. The closure of the global economy was presented as a means to “killing the virus”.
Sounds absurd. Closing down the real economy of planet Earth is not the “solution” but rather the “cause” of a process of worldwide destabilization and impoverishment, which in turn has an impact on patterns of morbidity and mortality. In this regard, what must be addressed is the causal relationship between economic variables (e.g. purchasing power, unemployment) and the state of health of the population.
The national economy combined with political, social and cultural institutions is the basis for the “reproduction of real life”: income, employment, production, trade, infrastructure, and social services.
Destabilizing the economy of planet Earth cannot constitute a “solution” to combating the virus. But that was the imposed “solution” which they want us to believe in. And that is what they are doing.
The Lockdown and the Process of Engineered Bankruptcy
There is an important relationship between the “real economy” and “Big Money”, namely the financial establishment.
What is ongoing is a process of concentration of wealth, whereby the financial establishment (i.e. the multi-billion dollar creditors) are slated to appropriate the real assets of both bankrupt companies as well as state assets.
The “real economy” constitutes “the economic landscape” of real economic activity: productive assets, agriculture, industry, goods and services, trade, investment, employment as well as social and cultural infrastructure including schools, hospitals, universities, museums, etc. The real economy at the global and national levels is being targeted by the lockdown and closure of economic activity.
The lockdown instructions transmitted to national governments have been conducive to the destabilization of “the national economic landscape” of numerous countries, which consists of a complex economic and social structure.
The “stay at home” lockdown prevents people from going to work. From one day to the next, it creates mass unemployment (worldwide). In turn, the lockdown is coupled with the closure of the entire sectors of the national economy.
The lockdown immediately contributes to the disengagement of human resources (labor) which in turn brings productive activity to a standstill.
The channels of supply and distribution are frozen, which eventually leads to potential shortages in the availability of commodities. In turn, several hundred million workers worldwide lose their jobs and their earnings.
While national governments have set up various “social safety nets” for the unemployed, the payment of wages and salaries by the employer is disrupted which in turn leads to a dramatic worldwide collapse in purchasing power.
It’s a payments crisis. Wages and salaries are not paid. Impoverished households are unable to purchase food, pay their rent or monthly mortgage. Personal and household debts (including credit card debts) go fly high. It’s a cumulative process.
This globalization of poverty leads to a decline in consumer demand which then backlashes on the productive system, leading to a further string of bankruptcies. Inevitably, the structure of international commodity trade is also affected.
Global Indebtedness
The Global Money financial institutions are the “creditors” of the real economy which is in crisis. The closure of the global economy starting in March 2020 has triggered a process of global indebtedness. Unprecedented in world history, a multi-trillion bonanza of dollar-denominated debts is hitting simultaneously the national economies of more than 190 countries.
The creditors will also seek to acquire ownership and/or control of “public wealth” including the social and economic assets of the state through a massive indebtedness project under the surveillance of creditor institutions including the IMF, the World Bank, the regional development banks, etc.
Under the so-called “new normal”, Great Reset put forth by the World Economic Forum (WEF), the creditors (including the billionaires) are intent upon buying out important sectors of the real economy as well as taking over bankrupt entities (see Chapter XIII).13
Crisis of the Global Economy. The Evidence
In the sections below, we briefly review the dramatic impacts of the closure of the global economy focusing on bankruptcies, global poverty, unemployment, the outbreak of famines as well as the collapse of the educational system.
Most of the figures quoted below are from the UN, governments and related sources, which tend to underestimate the seriousness of this ongoing global crisis, which is literally destroying people’s lives.
Indebtedness in all sectors of economic activity worldwide is the driving force. What is presented below is but the tip of the iceberg.
Bankruptcies
The wave of bankruptcies triggered by the closure of the world economy affects both small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) as well as large corporations. The evidence confirms that small and medium-sized enterprises are literally being wiped out.
According to a 2020 survey by the International Trade Centre, quoted by the OECD, pertaining to SMEs in 132 countries:
two-thirds of micro and small firms report that the crisis strongly affected their business operations, and one-fifth indicate the risk of shutting down permanently within three months. Based on several surveys in a variety of countries, McKinsey (2020) indicates that between 25% and 36% of small businesses could close down permanently from the disruption in the first four months of the pandemic. (OECD Report, emphasis added)14
According to Bloomberg:
“Over half of Europe’s small and medium-sized businesses say they face bankruptcy in the next year if revenues don’t pick up, underscoring the breadth of damage wrought by the Covid-19 crisis.
One in five companies in Italy and France anticipate filing for insolvency within six months, according to a McKinsey & Co. survey in August of more than 2,200 SMEs in Europe’s five largest economies.”15
The surveys tend to underestimate the magnitude of this unfolding catastrophe. The numbers are much larger than what is being reported.
In the US, the bankruptcy process is ongoing. According to a group of academics in a letter to Congress:
“We anticipate that a significant fraction of viable small businesses will be forced to liquidate, causing high and irreversible economic losses. “Workers will lose jobs even in otherwise viable businesses. ...
A run of defaults looks almost inevitable. At the end of the first quarter of this year, U.S. companies had amassed nearly $10.5 trillion in debt— by far the most since the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis began tracking the figure at the end of World War II. “An explosion in corporate debt,” Mr. Altman said.” (NYT, June, 16, 2020)16
With regard to small businesses in the US:
almost 90% of small businesses experienced a strong (51%) or moderate (38%) negative impact from the pandemic; 45% of businesses experienced disruptions in supply chains; 25% of businesses has less than 1-2 months cash reserves.“ (OECD)17
The results of a survey of over 5,800 small businesses in the United States:
... shows that 43% of responding businesses are already temporarily closed. On average, businesses reduced their employees by 40%. Three-quarters of respondents indicate they have two months or less in cash in reserve. ... (OECD) in a 2020 survey,18
“half of all US small business owners in the entire country believe that they may soon be forced to close down for good. Not even during the Great Depression of the 1930s did we see anything like this”.19
It should be noted that since the March 2020 lockdown (in both the US and Canada), both small and medium-sized enterprises as well as large corporations have received numerous handouts and loans under so-called emergency lending, which has contributed to delaying the actual filing of bankruptcy (in the US, see Chapter VII and Chapter XI). Worldwide, the filing of bankruptcy has been conveniently postponed following what the World Bank described as “trillions of dollars of financial support from governments” which are generously funded by Big Money creditors.
Global Unemployment
A massive worldwide contraction in employment is ongoing. In an August 2020 report, the International Labour Organization (ILO) confirms that:
The COVID-19 crisis has severely disrupted economies and labour markets in all world regions, with estimated losses of working hours equivalent to nearly 400 million full-time jobs in the second quarter of 2020, most of which are in emerging and developing countries... (ILO, 2020a). ...
Among the most vulnerable are the 1.6 billion informal economy workers, representing half of the global workforce, who are working in sectors experiencing major job losses or have seen their incomes seriously affected by lockdowns.
The COVID‐19 crisis is disproportionately affecting 1.25 billion workers in at-risk jobs, particularly in the hardest-hit sectors such as retail trade, accommodation and food services, and manufacturing (ILO, 2020b). Most of these workers are self-employed, in low- income jobs in the informal sector... Young people, for example, are experiencing multiple shocks including disruption to education and training, employment and income, in addition to greater difficulties in finding jobs.20
The ILO does not in any way explain the political causes of mass unemployment, resulting from actions taken by national governments, allegedly with a view to resolving the COVID pandemic. Moreover, the ILO tends to underestimate both the levels as well as the dramatic increase in unemployment.
Global Unemployment Is Slated to Rise in 2022-23
The pandemic is presented as the cause of unemployment. According to the ILO:
Global unemployment is expected to remain above pre-COVID-19 levels until at least 2023.
The 2022 level is estimated at 207 million, compared to 186 million in 2019.21
The ILO acknowledges that the overall impact on employment is not revealed by the above projections of global unemployment, “because many people have left the labour force”.
What is at stake is that large sectors of the labor force are the victims of bankruptcies as well as discriminatory policy mandates which have marginalized them from the labour market.
National governments remain under the control of global creditors. What is contemplated for the post-COVID era is the implementation of massive austerity measures including the cancellation of workers’ benefits and social safety nets.
Unemployment in the US
In the US, “more than 30 million people, over 15% of the workforce, applied for unemployment benefits... ” in the immediate wake of the March 2020 lockdown. (CSM, May 6, 2020)22
Announced in early December 2020, “More than 10 million Americans are projected to lose their unemployment benefits the day after Christmas [2020] unless Congress acts to extend key pandemic- related programs – a prospect that as of now looks uncertain at best.” (US News and World Report)23
The cliff edge looms as coronavirus cases surge around the country and applications for unemployment benefits rise with states and localities reimposing virus-related restrictions. The lapse is also set to occur as protections for renters, student loan borrowers and homeowners expire – a potential devastating confluence of events for both individuals, whose savings have ravaged by the pandemic, and the economy at large, which is gradually clawing its way back from the coronavirus-induced recession.
When the programs lapse at the end of December [2020], an estimated 12 million people could lose jobless benefits, according to the Century Foundation. (US News and World Report)24
During the most severe Main Street economic collapse in US history — with over one- fourth of working-age Americans jobless — an additional calamity looms:
According to Census Bureau estimates, 30 to 40 million Americans face possible eviction in 2021-22 for lack of income to pay rent or service mortgages.
Without federal aid or an extended rent moratorium, a calamity of biblical proportions may unfold in the coming months. (Stephen Lendman)25
Unemployment in the European Union (EU)
“Unemployment across the whole of the European Union is expected to rise to nine percent in 2020, in the wake of the Coronavirus pandemic and subsequent lockdowns enforced by national governments”.26
According to official EU figures:
Greece, Spain and Portugal ... have once again seen large rises in youth unemployment since the start of the pandemic. Greece saw a surge from 31.7 percent in March [2020] to 39.3 percent in June [2020], while Spain and Portugal had similar increases, from 33.9 percent to 41.7 percent and 20.6 percent to 27.4 percent, respectively.27
Unemployment in Latin America
In Latin America, the average unemployment rate was estimated at 8.1 percent at the end of 2019. The ILO states that it could rise by a modest 4 to 5 percentage points to 41 million unemployed.28
In absolute numbers, these rates imply that the number of people who are looking for jobs but are not hired rose from 26 million before the pandemic to 41 million in 2020, as announced by ILO experts.
These estimates of the ILO and the World Bank are misleading. According to the Inter American Development Bank (IDB), the increase in unemployment for the Latin American region was of the order of 24 million in 2020, with job losses in Colombia of the order of 3.6 million, Brazil 7.0 million and Mexico 7.0 million.29
Even these figures tend to underestimate the dramatic increase in unemployment. And the situation has evolved in 2021-23, following partial lockdowns which have triggered a renewed wave of bankruptcies.
According to a survey conducted by the Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), the increase in unemployment in Mexico was of the order of 12.5 million in April 2020, i.e. in the month following the March 11, 2020 lockdown and closure of the national economy.30
The Outbreak of Famines
Poverty and chronic undernourishment is a pre-existing condition.
First, there is a long-term historical process of macroeconomic policy reform and global economic restructuring which has contributed to depressing the standard living worldwide in both the developing and developed countries.
Second, these pre-existing historical conditions of mass poverty have been exacerbated and aggravated by the imposition of the COVID lockdown.
With large sectors of the world population already well below the poverty line prior to the March 2020 COVID-19 lockdown, the recent hikes in the prices of basic food staples are devastating.
According to the World Food Programme (WFP), “690 million people do not have enough to eat while 130 million additional people risk being pushed to the brink of starvation.” (November 2020 statement)
These figures are questionable. Both the FAO and the WFP have failed to address the central role of the lockdown and closure of national economies as a “shock mechanism” which simultaneously triggers mass poverty coupled with the destabilization of agricultural production in both developing and developed countries, in all major regions of the world.
The underlying causality is simply not addressed. Climate and conflict analysis take precedence:
“We are seeing a catastrophe unfold before our very eyes. Famine – driven by conflict, and fuelled by climate shocks and the COVID-19 hunger pandemic – is knocking on the door for millions of families.” (David Beasley, Executive director of the WFP)
The FAO Report
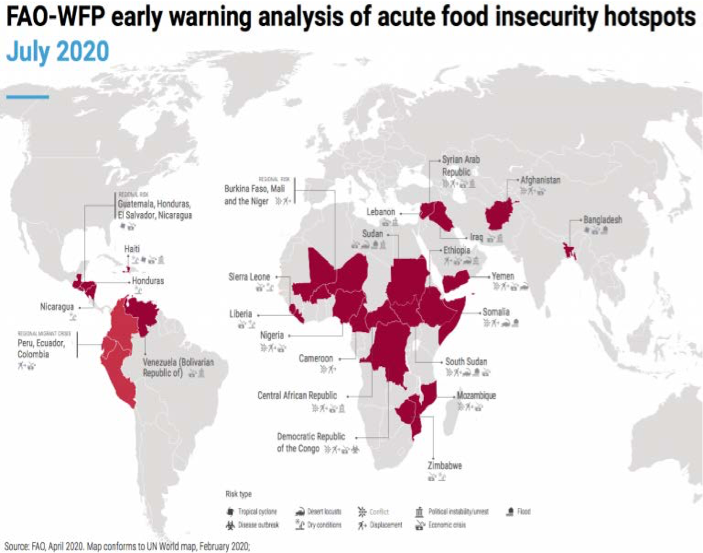
Famines have erupted in at least 25 developing countries according to the FAO. It’s an incomplete study: most of Asia and Latin America, Europe, the Middle East and North America are not included (see map below):
“The UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Food Programme (WFP) identifies 27 countries that are on the frontline of impending COVID-19-driven food crises, as the pandemic’s knock-on effects aggravate pre-existing drivers of hunger.
No world region is immune, from Afghanistan and Bangladesh in Asia, to Haiti, Venezuela and Central America, to Iraq, Lebanon, Sudan and Syria in the Middle East to Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Liberia Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Mozambique, Sierra Leone and Zimbabwe in Africa.
The joint analysis by FAO and WFP warns these “hotspot countries” are at high risk of – and in some cases are already seeing – significant food security deteriorations in the coming months, including rising numbers of people pushed into acute hunger.”
Source: FAO, April 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has potentially far-reaching and multifaceted indirect impacts on societies and economies, which could last long after the health emergency is over. These could aggravate existing instabilities or crises, or lead to new ones with repercussions on food security, nutrition and livelihoods.
With over two billion people, or 62 percent of all those working worldwide, employed in the informal economy according to ILO data, millions of people face a growing risk of hunger. Earnings for informal workers are estimated to have declined by 82 percent, with Africa and Latin America to face the largest decline (ILO 2020). (FAO, p. 6)31
Global Famine. Acute Hunger in 80 Countries
A World Food Programme (WFP) November 2021 report points to Global Famine and “Acute Hunger in 80 Countries”:
Global hunger continues to rise at an alarming rate: our latest estimates show that 282.7 million people across 80 countries are experiencing extreme levels of acute hunger. This represents an increase of around 110 percent compared to 2019 (when 135 million people in 58 countries were classified as acutely food insecure).
This “guesstimate” of 287.7 million cases of acute hunger borders on ridicule and “fake statistics”. Mass poverty is extensive worldwide. The “estimate” is based on the following concept, which is put forth by the World Food Programme (a UN body) as a humanitarian and compassionate criterion:
“one meal a day, the basic needed to survive – costing US$0.43 per person per day”. (WFP, p 1)
Ask Bill Gates, who is actively buying up bankrupt family farms: “how much did your lunch cost”? The recent hikes in food prices are contributing in a very real sense to “eliminating the poor” through “starvation deaths”. In the words of Henry Kissinger:
“Control oil and you control nations; control food and you control the people.”
In this regard, Kissinger had intimated, in the context of the “1974 National Security Study Memorandum 200: Implications of Worldwide Population Growth for U.S. Security and Overseas Interests,” that the recurrence of famines could constitute a de facto instrument of population control. It’s part of the WEF’s eugenics agenda.
Famine and Despair in India
The social and economic impacts of the March 11, 2020 lockdown in India were devastating, triggering a wave of famine and despair. “Millions of people who lost their income now face increased poverty and hunger, in a country where even before the pandemic 50 percent of all children suffered from malnourishment”.32
In late November 2020, the largest general strike in the country’s history was carried out against the Modi government with more than 200 million workers and farmers. According to the Mumbai University and College Teachers’ Union:
This strike is against the devastating health and economic crisis unleashed by COVID-19 and the lockdown on the working people of the country. This has been further aggravated by a series of anti-people legislations on agriculture and the labour code enacted by the central government. Along with these measures, the National Education Policy (NEP) imposed on the nation during the pandemic will further cause irreparable harm to the equity of and access to education.33
According to Left Voice:
“The pandemic has spread from major cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, and other urban centers to rural areas where public health care is scarce or non-existent. The Modi government has handled the pandemic by prioritizing the profits of big business and protecting the fortunes of billionaires over protecting the lives and livelihoods of workers.”34
“Food Insecurity” in the US
Undernourishment and so-called “food insecurity” are not limited to developing countries.
The terminology is not quite the same. “Famine” in America which today is a reality is rarely mentioned. Neither is the lockdown (confinement of the labor force) acknowledged as a mechanism which has triggered so-called “food insecurity”.
The US Department of Agriculture defines “food insecurity” as “a household-level economic and social condition of limited or uncertain access to adequate food”.
“Hunger” is defined as “an individual-level physiological condition that may result from food insecurity”. “Famine” does appear in the USDA glossary.
Recent estimates by Feeding America suggest that one in seven Americans representing 45 million people in 2020, including 15 million children, experienced “food insecurity”:
Before the start of the pandemic, the overall food insecurity rate had reached its lowest point since it began to be measured in the 1990s, but those improvements were being upended by the pandemic.35
According to Stephen Lendman:
“Around one in four US households experienced food insecurity this year [2020]— over 27% of households with children.
A Northwestern University Institute for Policy Research study estimates the number of food insecure households with children at nearly 30%. Black families are twice as food insecure as their white counterparts. Latino households are also disproportionately affected.”36
The Billionaires’ “Solution to Global Famine”?
In a bitter irony, the World Food Programme (WFP) has announced that the billionaire philanthropists (including the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Rockefeller Foundation, et al.), who have enriched themselves in the course of the COVID-19 crisis, have generously come to the rescue of 42 million people affected by famine.
Bear in mind, this process of global impoverishment is the direct consequence of billionaire enrichment invariably conducted through fake science and fraudulent transactions (see Chapter V).
According to Oxfam, “For every new billionaire created during the pandemic. ... millions of people were pushed into extreme poverty”.
“Billionaires gathered in Davos have enjoyed an obscene surge in their fortunes over the last two years. The pandemic and now the steep rise in food and energy prices have been a bonanza for the wealthiest, while millions of people face hunger and poverty as the cost living shoots up.” (Oxfam)
Education: The Impacts on Our Children
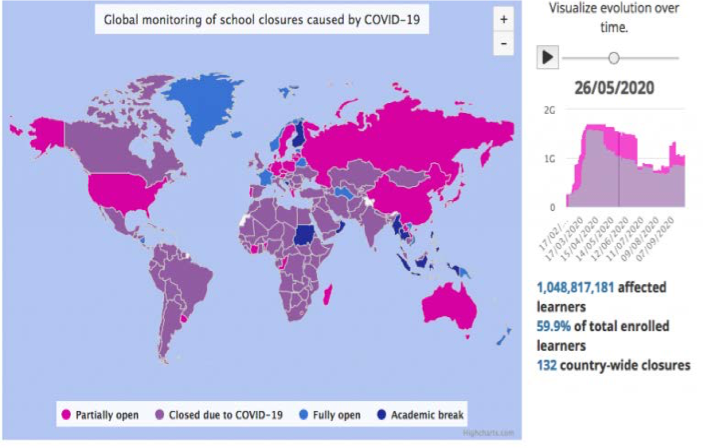
The very foundations of civil society are threatened. UNICEF estimates that 1.6 billion children and adolescents were affected by the closure of schools worldwide.37
“As the COVID-19 pandemic has spread across the globe, a majority of countries have announced the temporary closure of schools, impacting more than 91 per cent of students worldwide... Never before have so many children been out of school at the same time...”
Colleges and universities are also paralysed. Students are denied the right to education. While UNESCO confirms that more than one billion learners are affected, it offers no concrete solution or critique. The official narrative of the so-called “public/private partnership” imposed on national governments has been adopted at face value.38
School closures were carried out in 132 countries. See diagram below (UNESCO, May 2020).
Screenshot from UNESCO
The above review of the economic and social impacts points to a complex process. Large sectors of the world population have been precipitated into poverty and despair. The various agencies of the United Nations quoted above tend to skim the surface. The underlying causes are simply not addressed.
The Global Travel and Tourism Economy
Prior to the corona crisis, travel and tourism represented a major share of the global economy: approximately ten percent of global GDP with an estimated workforce of more than 320 million jobs worldwide.39
Travel and tourism industry, which includes airlines, airport facilities, land transportation, hotels, resorts, restaurants, museums, concert halls, parks, and a variety of urban services, has been precipitated into bankruptcy resulting in mass unemployment.
The economic and social impacts are devastating particularly in countries which have a sizeable tourist economy (e.g. Italy, France, Switzerland, Thailand, Vietnam, Mexico, Cuba, The Dominican Republic, Peru, and Panama, among others).
The estimated loss of jobs in the tourism industry is estimated to be of the order of 100 million worldwide (November 2020 report, see also IMF report).40
Job Losses in the US
According to the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), a “staggering 9.2 million jobs could be lost in the U.S. ... if barriers to global travel remain in place”. The WTTC estimates that more than half of all jobs supported by the sector in the U.S. in 2019 are slated to be lost. Between 10.8 million and 13.8 million jobs within the Travel and Tourism sector “are at serious risk”.41
Bankruptcies
While the restrictions on air travel coupled with the March 11, 2020 lockdown triggered the demise of smaller regional airlines, in the course of the 2020-2022, a large number of national flag carriers have been precipitated into a de facto bankruptcy situation, including Aero-Mexico, Avianca, and South African Airlines, among others. According to a report, “43 commercial airlines have failed since January 2020, ... completely ceasing or suspended operations” in 2020. There was also a backlash on the production of civilian aircraft.42
Trump’s suspension of air travel to China on January 31, 2020 based on five COVID-19 confirmed positive cases in the U.S. played a key role in setting the stage for the air travel and tourism crisis, which at the time of writing is still ongoing.
The lockdown has also undermined the largest transport infrastructure project in Europe, namely the underground tunnel between the UK and continental Europe. The Eurostar was precipitated into a situation of de facto bankruptcy.
All of these disruptions in international travel are presented to public opinion as a means to combating the killer virus. It’s a big lie.
Bankrupt hotel chains and major airlines in all likelihood will be “picked up” at rock-bottom prices by the multi-billionaires.
The Shanghai 2022 COVID Zero Tolerance Mandate. The Destabilization of China’s Export Economy?
Starting in late March, early April 2022, the Chinese government ordered the lockdown pertaining to Shanghai, a port city of 26 million people.
The confinement of Shanghai’s labour force was carried out under a “COVID Zero Tolerance Mandate”: “At least 38,000 medical workers from across China have been deployed to aid Shanghai ... in the fight against the Omicron variant...” (Global Times)43
Visibly, China’s health authorities had endorsed the Fauci-Gates “fake science” lockdown consensus without batting an eyelid. China’s Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC) is headed by Dr. George Gao Fu, a colleague of Anthony Fauci, et al. Anthony Fauci is Dr. Gao Fu’s mentor.
China’s Zero Tolerance COVID Mandate was a “copy and paste” of the March 11, 2020 lockdown (based on “fake science”) sponsored by Anthony Fauci, Bill Gates, et al. under the auspices of the WHO (in close consultation with the World Economic Forum). China’s Zero Tolerance COVID Mandate is predicated on a fear campaign.
In mid-July 2022, China’s health authorities announced that several major urban areas had been instructed to implement the COVID Zero Tolerance Mandate as a means to combating the “highly-transmissible Omicron BA.5 subvariant”.
Image: Dr. George Gao Fu (by China News Network, licensed under CC BY 3.0)
The labour force has been confined in a large number of industrial cities thereby leading to economic and social chaos as well as a dramatic decline in economic activity. According to Reuters:
The BA.5 [subvariant] lineage, spreading fast in many other countries, has been detected in cities such as Xian in the province of Shaanxi and Dalian in Liaoning province, ... It was first found in China on May 13 in a patient who had flown to Shanghai from Uganda, the China Center for Disease Prevention and Control said, with no local infections linked to the case that month.44
Did that “patient” from Uganda take the PCR test upon his return to China?
Variants and sub-variants cannot under any circumstances be detected by the PCR test (the original SARS-CoV-2 virus cannot be detected by the PCR test, see Chapter III).
A large number of urban areas were closed down in major regions of China. On July 11, 2022, China’s National Heath Commission confirmed the following data for mainland China:
a total of 352 new domestically transmitted COVID infections recorded on
July 10, 46 new symptomatic cases, and
306 new asymptomatic cases.
46 new symptomatic cases out of a population of 1.45 billion people does not justify closing down China’s major urban areas.
Economic Destabilization: Shanghai and the Global Economy
The impacts of these measures put forth by China’s National Health Commission and China’s CCDC have precipitated China’s supply chains into jeopardy.
“COVID Zero Tolerance” has contributed to destabilizing Shanghai’s financial sector as well as its buoyant export economy. It has also contributed to undermining domestic transport and commodity supply lines.
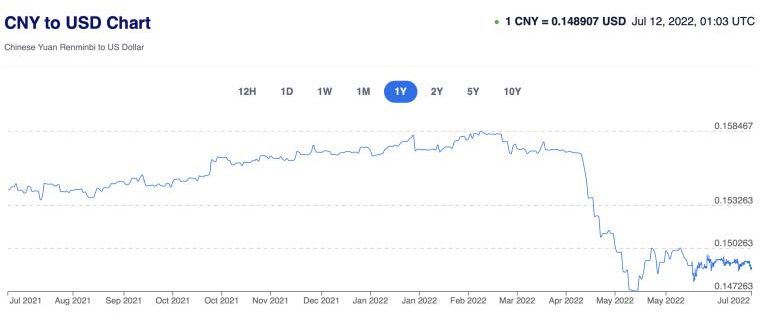
Since mid-April 2022 (coinciding with the lockdown of Shanghai), the Yuan (CNY) declined abruptly against the US dollar (USD).
Chinese Yuan Renminbi to US Dollar Exchange Rate Chart (Source: Xe)
The volume of commodity trade in and out of the Port of Shanghai (and other major port cities) has subsided, which inevitably has a bearing on the availability of “Made in China” commodities worldwide.
Made in China goods (By Thi Nguyen 2021, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0)
Made in China
“Made in China” is the backbone of retail trade which indelibly sustains household consumption in virtually all major commodity categories from clothing, footwear, to hardware, electronics, mobile phones, TV sets, toys, jewelries, household fixtures, food, etc.
Ask the American consumer: the list is long.
Importing from China is a lucrative multi-trillion dollar operation. It is the source of tremendous profit and wealth in the US because consumer commodities imported from China’s low wage economy are often sold at the retail level more than ten times their factory price.
Global commodity trade at wholesale and retail levels is in crisis. The potential impacts in all major regions of the world are devastating — worldwide scarcities of essential consumer goods coupled with inflationary pressures.
These developments also affect China’s sovereignty as a nation-state with a weakened economy, not to mention its Belt and Road initiative.
In the context of the current crisis, including Washington’s “Pivot to Asia”, there are serious geopolitical implications which have a direct bearing on the confrontation between China and the US.
For further details see Michel Chossudovsky, The Shanghai “COVID Zero Tolerance Mandate”. Engineered Depression of China’s Economy?
Automobile Industry at a Standstill: Engineered Shortage in the Production of Semi-conductors?
The automobile industry worldwide experienced a 15% decline in production in 2020. The decline in 2021-22 is significant, largely affecting production in Japan, South Korea and China.
This decline has been accentuated by a shortage in the availability of semi-conductors:
“Automakers, which rely on dozens of chips to build a single vehicle, have been particularly hard hit.
The debacle is likely to cost the auto industry $450 billion in global sales ... In September 2021 Toyota was forced to slash production at 14 factories in Japan over a lack of semiconductors. Some of the cuts will continue into October due to a lack of components from Southeast Asia, Toyota has said.” (Washington Post, September 2021)46
Semi-conductors constitute a strategic commodity, used in a variety of sectors including electronics, medical devices, electronic and communications networks, etc.
There are indications of possible manipulations, which have led to artificial shortages of semi- conductors affecting a number of key sectors of the global economy.
There are geopolitical implications. The world’s largest semi-conductor producer is the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC).
Global “Supply Chain Disruptions” and Demand Relations
The lockdowns from March 11, 2020 onwards have triggered a process of worldwide economic destabilization which directly affects both “supply” and “demand” relations. It’s the most serious economic crisis in world history affecting simultaneously more than 190 countries.
“Supply” pertains to the production of goods and services, namely the activities of the “real economy”. “Demand” pertains to the ability of households given their purchasing power to acquire essential goods and services.
Both supply and demand relations are in jeopardy.
Worldwide, large sectors of industry, agriculture and urban services stand idle. The lockdown policies initiated in March 2020 have triggered bankruptcies and unemployment, which in turn have been conducive to a process of disengagement of human resources (labor) and productive assets from the economic landscape.
On the supply side, a massive contraction in the production and availability of goods and services (commodities) is unfolding. Entire sectors of the global economy are “not producing”, scarcities of certain commodities and services have emerged. In turn, the channels of transportation by land and sea (e.g. container trade) have been disrupted since March 2020.
On the demand side, mass unemployment and poverty triggered by the lockdown policies has contributed to an unprecedented collapse in purchasing power (of families and households worldwide), which in turn has led to the collapse in the demand for goods and services. Poverty is rampant, large sectors of the world population do not have money to buy food and essential consumer goods.
Contraction of production (supply) coupled with the collapse of purchasing power (demand) is conducive to a deep-seated worldwide economic depression coupled with inflationary pressures.
In turn, the collapse in purchasing power resulting from mass unemployment has led to a mounting personal debt crisis including the inability to meet monthly rent and mortgage payments. This process eventually leads to a confiscation of real assets.
In the US, 68 percent of those who were behind on rent (May 2021 figures) had become unemployed as a result of the lockdown.47
These developments are casually blamed on the “pandemic’s economic fallout” without analyzing how the failed lockdown policies were instrumental in triggering economic chaos and unemployment worldwide.
The Fiscal Crisis of the Nation-State
State-funded public sector activities including health, education, culture, sports and the arts are in jeopardy. Meanwhile, in the US, the Biden administration has favored a massive increase in military and security-related expenditures as well as biotechnology with generous handouts to Big Pharma and the Military-Industrial Complex.
Since the onset of the corona crisis, the public debt in country after country has gone fly high largely precipitated by economic chaos.
Bankrupt companies no longer pay taxes. Unemployed workers (without earnings) no longer pay taxes. Tax dollars are no longer coming into the coffers of the state.
The increase in global unemployment and poverty coupled with bankruptcies have led to an unprecedented fiscal crisis.
In turn, government revenue has been redirected to funding corporate handouts.
The private appropriation of wealth has precipitated a global debt crisis. In country after country, the public debt has skyrocketed.
Massive Austerity Measures, Global Insolvency
Generous handouts and social safety nets have been used by national governments as a means to enforcing compliance and acceptance of the COVID-19 mandates. These handouts (including loans at 0%) are eventually slated to be abolished and replaced by the most drastic austerity measures in world history.
An unpayable multi-trillion dollar public debt is unfolding worldwide, coupled with a process which we might describe as “global insolvency”.
The creditors of the state are “Big Money”. Ultimately, they call the shots.
The enrichment of the billionaire class has also contributed to the destabilization of the nation-state (see Chapter V).
What is also unfolding is the “privatization of the nation-state” including the progressive demise of the “welfare state” and its public institutions (education, health, culture).
Endnotes
1. Allison Aubrey, January 31, 2020. Trump Declares Coronavirus A Public Health Emergency And Restricts Travel From China. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2020/01/31/801686524/trump-declares-coronavirus-a-public-health- emergency-and-restricts-travel-from-c
2. The Economist, February 17, 2020. The coronavirus spreads racism against—and among—ethnic Chinese. https:// www.economist.com/china/2020/02/17/the-coronavirus-spreads-racism-against-and-among-ethnic-chinese
3. Wallis Wang, February 13, 2020. Britain’s Chinese community faces racism over coronavirus outbreak. https:// www.scmp.com/video/world/3050436/britains-chinese-community-faces-racism-over-coronavirus-outbreak
4. Prof Michel Chossudovsky, November 5, 2020. The Corona Pandemic and Trump’s Trade War against China: America’s Dependence on “Made in China”. Potential Disruption of the US Economy. https://www.globalresearch.ca/the-corona- pandemic-and-trumps-trade-war-against-china-americas-dependence-on-made-in-china-potential-disruption-of-the-us- economy/5713552
5. Financial Times, May 11, 2020. US-China economic decoupling accelerates in first quarter of 2020. https:// www.ft.com/content/115fc14f-4a8a-45da-8688-c59605a5191a
6. Joe Mcdonald, January 14, 2022. China’s Trade Surplus Hit Record in 2021—With Exports Jumping 30% Amid Pandemic Demand. https://time.com/6139334/china-record-trade-surplus-2021/
7. WHO, February 20, 2020. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 on 20 February 2020. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on- covid-19-on-20-february-2020
8. WHO, n.d. Declarations of Interest. https://www.who.int/about/ethics/declarations-of-interest
9. Maggie Fitzgerald, September 17, 2019. More than 60% of Bill Gates’ wealth is invested in stocks. https://
www.cnbc.com/2019/09/17/bill-gates-gave-away-35-billion-this-year-but-net-worth-didnt-drop.html
10. Fred Imbert, Maggie Fitzgerald, et al., February 28, 2020. Stock market Friday recap: Dow loses 3,500 points on week, closes off lows, Fed pledges support. https://www.cnbc.com/2020/02/28/stock-market-live-updates-dow-loses-3200-points- and-counting-on-week-bond-yields-collapsing.html
11. WHO, March 12, 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 52. https://www.who.int/docs/default- source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200312-sitrep-52-covid-19.pdf
12. Pipa Stevens, Maggie Fitzgerald, et al., March 12, 2020. Stock market live Thursday: Dow tanks 2,300 in worst day since Black Monday, S&P 500 bear market. https://www.cnbc.com/2020/03/12/stock-market-today-live.html
13. WEF, n.d. The Great Reset. https://www.weforum.org/great-reset/
14. OECD, July 15, 2020. Coronavirus (COVID-19): SME policy responses. https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/coronavirus-covid-19-sme-policy-responses-04440101/
15. See this: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-10-22/half-of-europe-s-smaller-businesses-risk-bankruptcy- within-year
16. See this: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/18/business/corporate-bankruptcy-coronavirus.html
17. OECD, July 15, 2020. Coronavirus (COVID-19): SME policy responses. https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/coronavirus-covid-19-sme-policy-responses-04440101/
18. Michael Snyder, December 10, 2020. 48% Of U.S. Small Businesses Fear that They May be Forced to “Shut Down Permanently” Soon.
https://www.globalresearch.ca/48-us-small-businesses-fear-forced-shut-down-permanently- soon/5732050
19. Chuck Casto, November 25, 2020. Alignable: 48% Of Small Businesses Risk Closing in Q4, New Poll Says. https:// www.alignable.com/forum/alignable-48-of-small-businesses-risk-closing-for-good-new-poll
20. ILO, September 23, 2020. COVID-19 leads to massive labour income losses worldwide.
https://www.ilo.org/global/about- the-cilo/newsroom/news/WCMS_755875/lang–en/index.htm
21. ILO, January 17, 2022. ILO downgrades labour market recovery forecast for 2022. https://www.ilo.org/global/about-the-ilo/ newsroom/news/WCMS_834117/lang–en/index.htm
22. Ned Temko, May 6, 2020. No jobs, so what future? Half the world’s workforce on the edge. https://www.csmonitor.com/ World/2020/0506/No-jobs-so-what-future-Half-the-world-s-workforce-on-the-edge
23. Claire Hansen, December 2, 2020. Some 12 Million to Lose Unemployment Aid After Christmas With Stimulus Still Uncertain. https://www.usnews.com/news/national-news/articles/2020-12-02/some-12-million-to-lose-unemployment-aid-after- christmas-with-stimulus-still-uncertain
24. Ibid.
25. Stephen Lendman, December 2, 2020. Millions of Americans Vulnerable to Eviction.
https://www.globalresearch.ca/millions-americans-vulnerable-eviction/5730985
26. Statista, January 2022. Unemployment rate in selected European countries as of November 2021.
https:// www.statista.com/statistics/1115276/unemployment-in-europe-by-country/
27. James Poulter, September 15, 2020. Europe Is Facing a Youth Unemployment Crisis.
https://www.vice.com/en/article/ v7gknm/europe-is-facing-a-youth-unemployment-crisis
28. ILO, July 1, 2020. ILO: Sharp rise in unemployment in Latin America and the Caribbean leaves millions without income.
https://www.ilo.org/caribbean/newsroom/WCMS_749692/lang–en/index.htm
29. Semana, August 19, 2020. Colombia, el tercer país que más empleos perdió en América Latina.
https:// www.semana.com/empresas/confidencias-on- line/articulo/empleos-que-mas-se-perdieron-en-america-latina-segun-el-bid/296265/
30. Forbes, June 3, 2020. Desempleo en México alcanza a casi 25% de la población: Heath.
https://www.forbes.com.mx/ economia-desempleo-mexico-casi-25-poblacion-heath/
31. FAO and WFP, July 2020. FAO-WFP early warning analysis of acute food insecurity hotspots.
https://www.fao.org/3/ cb0258en/CB0258EN.pdf
32. Global Research News, December 4, 2020. India: Largest Strike in World History : Over 200 Million Workers and Farmers Protest against Poverty and Unemployment Triggered by Covid Lockdown.
https://www.globalresearch.ca/india-largest-strike- in-world-history-over-200-million-workers-and-farmers-paralyze-india/5731395
33. Ibid. 34. Ibid.
35. Feeding America, March 2021. The Impact of the Coronavirus on Food Insecurity in 2020 & 2021.
https:// www.feedingamerica.org/sites/default/files/2021-03/National%20Projections%20Brief_3.9.2021_0.pdf
36. Stephen Lendman, October 3, 2020. Covid Crisis Has Triggered Mass Unemployment in America: Over One Million UI Claims in the US for 28 Straight Weeks. https://www.globalresearch.ca/over-one-million-ui-claims-us-28-straight- weeks/5725527
37. Jason Miks and John McIlwaine, April 20, 2020. Keeping the world’s children learning through COVID-19. https:// www.unicef.org/coronavirus/keeping-worlds-children-learning-through-covid-19
38. UNESCO, n.d. Education: From disruption to recovery. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
39 Adam Behsudi, December 2020. Tourism-dependent economies are among those harmed the most by the
pandemic. https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2020/12/impact-of-the-pandemic-on-tourism-behsudi.htm
40. Margaux MacDonald, Roberto Piazza, et al., September 2, 2020. A Simple Guide to Estimating the Impact of COVID-19 on Travel and Hospitality Activity. PDF Link
41. World Travel and Tourism Council, November 11, 2020. U.S. looks set to lose 9.2 million jobs in 2020 due to COVID-19 and travel restrictions, says WTTC. https://wttc.org/Portals/0/Documents/Press%20Releases/US-looks-set-to-lose-9-million- jobs-in-2020-due-to-COVID-19-and-travel-restrictions.pdf
42. Abigail Ng, October 8, 2020. Over 40 airlines have failed so far this year — and more are set to come. https:// www.cnbc.com/2020/10/08/over-40-airlines-have-failed-in-2020-so-far-and-more-are-set-to-come.html
43. Global Times, April 4, 2022. Over 38k medical workers deployed to aid Shanghai in Omicron battle, the highest number since Wuhan in early 2020. https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202204/1257497.shtml
44. Roxanne Liu& Ryan Woo, July 11, 2022. Update 3-Shanghai plans more COVID testing amid fresh curbs across China. https://ca.news.yahoo.com/1-shanghai-braces-more-mass-040242739.html
45. Ibid.
46. Jeanne Whalen, September 23, 2021. Semiconductor shortage that has hobbled manufacturing worldwide is getting worse. https://www.washingtonpost.com/us-policy/2021/09/23/chip-shortage-forecast-automakers/
47. Sarah Treuhaft, Michelle Huang, et al., September 16, 2021. Rent Debt in America: Stabilizing Renters Is Key to Equitable Recovery. https://nationalequityatlas.org/rent-debt-in-america








and STILL the unthinking comatose sheeple refuse to see the obvious. the biggest psyops in human history. instead of rising up against the psychopaths in WEF and the govts involved,the mindless populations believe all will be good again as soon as they play the one armed bandit of voting.
Thank you for this .